Essential CPR Techniques You Need to Learn
Knowing CPR can mean the difference between life and death. CPR stands for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation, and it’s a lifesaving technique used in emergencies when someone’s heartbeat or breathing has stopped. CPR helps keep oxygenated blood flowing to the brain and other vital organs until professional help arrives. This initial support is crucial as it can prevent brain damage and improve the chances of survival.
In this article, we will dive into the basics of CPR, provide a step-by-step guide to performing it, and share tips for ensuring your techniques are effective. We’ll also cover real-life scenarios where CPR might be needed and discuss the importance of getting proper training and certification.
1. What Is CPR and When to Use It
CPR, or Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation, is a life-saving technique that is used in emergencies when someone's heart or breathing has stopped. This can happen due to various reasons like heart attacks, drowning, choking, or severe injuries. The main goal of CPR is to keep blood flowing to vital organs, especially the brain until advanced medical care can be provided. Effective CPR can significantly increase the chances of survival and reduce the risk of permanent brain damage.
CPR consists of chest compressions and rescue breaths. Chest compressions help circulate the blood, while rescue breaths provide oxygen to the lungs. Performing CPR immediately after cardiac arrest can double or even triple a person's chances of survival. It's a crucial skill that everyone should learn because emergencies can happen anytime and anywhere.
2. Differences Between Adult, Child, and Infant CPR
CPR techniques differ depending on the age and size of the person in need:
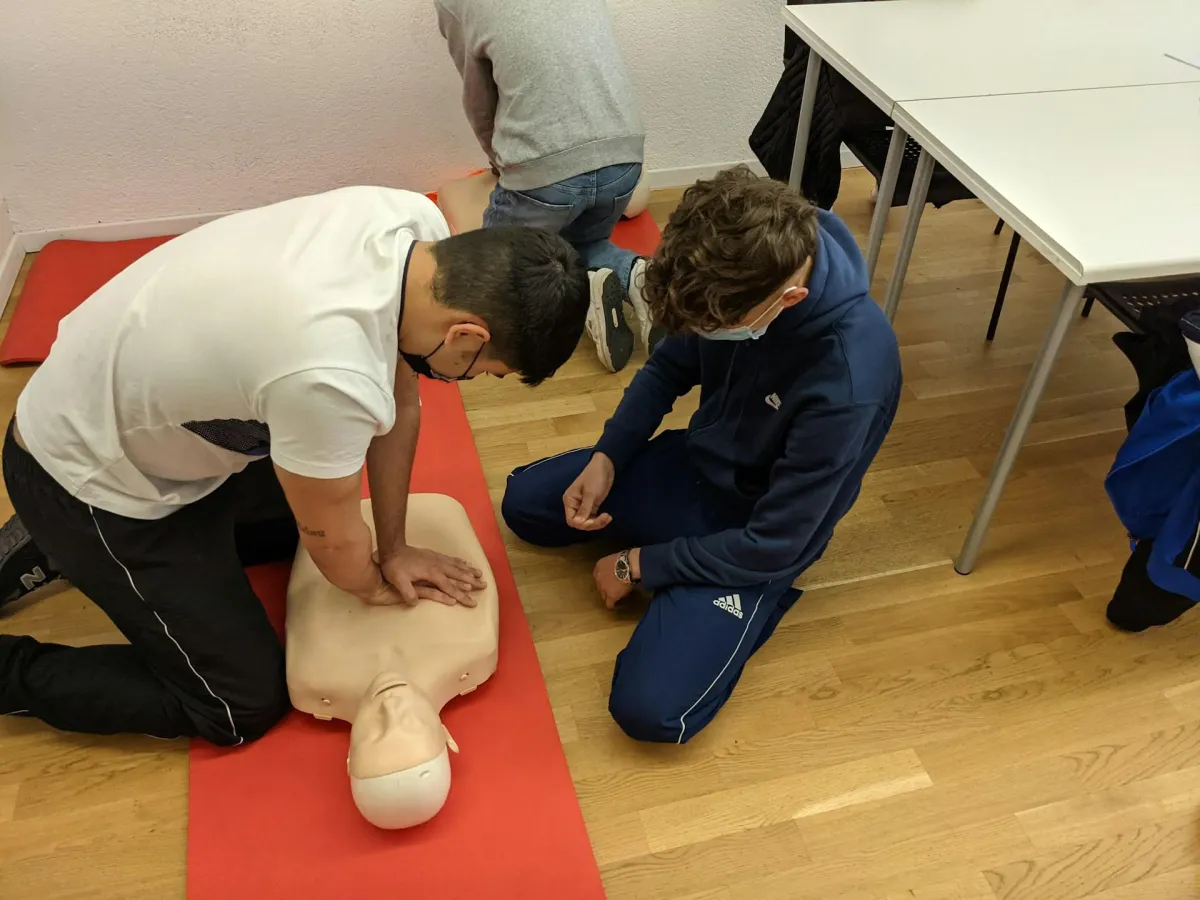
Adult CPR: For adults, use both hands placed one on top of the other at the center of the chest. Push hard and fast, at least 2 inches deep, and at a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute. After every 30 compressions, give 2 rescue breaths by tilting the head back, lifting the chin, and making a seal over the mouth.
Child CPR (Ages 1-8): Use one hand instead of two for chest compressions. Press down about 2 inches in depth and follow the same compression rate as for adults. Like adult CPR, give 2 rescue breaths after every 30 compressions.
Infant CPR (Under 1 year old): Use two fingers placed just below the nipple line and press down about 1.5 inches deep. The compression rate remains the same at 100 to 120 compressions per minute. Rescue breaths are given by covering the infant's mouth and nose with your mouth and delivering gentle breaths.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Performing CPR
Assessing the Situation and Ensuring Safety
Before you start performing CPR, it's important to assess the situation. Make sure the area is safe for both you and the victim. If the environment is hazardous, move the victim to a safer location if possible. Check if the person is responsive by tapping them and shouting, "Are you okay?" If there is no response, call 911 immediately or ask someone nearby to do so.
Next, check for breathing. Look for chest movements, listen for breath sounds, and see if you can feel their breath on your cheek. If the person is not breathing or only gasping, it's time to start CPR.
Detailed Steps for Chest Compressions and Rescue Breaths
Chest Compressions
- Kneel beside the person.
- For adults and children, place your hands (or hand) in the center of the chest. For infants, use two fingers.
- Press down hard and fast, keeping a steady rhythm of 100 to 120 compressions per minute. Let the chest rise fully between compressions.
Rescue Breaths
- After 30 compressions, give 2 rescue breaths.
- Tilt the person's head back slightly by lifting the chin.
- Pinch the nose shut and make a complete seal over their mouth with yours.
- Blow into the mouth for about 1 second, watching to see if the chest rises. Give a second breath if the chest rises with the first.
- For infants, cover both the nose and mouth with your mouth and give gentle puffs.
Repeat the cycle of 30 compressions and 2 breaths until medical help arrives, an AED (Automated External Defibrillator) is available, or the person shows signs of life like breathing or movement. Knowing these steps can prepare you to act confidently and effectively in emergency situations.
4. Important Techniques and Tips for Effective CPR
Proper Hand Placement and Compression Depth
Performing CPR correctly ensures that it's effective. For adults, place the heel of your hand on the center of the chest, right between the nipples. Put your other hand on top and interlock your fingers. Your elbows should be straight, and your shoulders lined up directly over your hands. For children, use only one hand in the same location. For infants, use two fingers just below the nipple line.
Compression depth is also crucial. For adults, aim for at least 2 inches deep. For children, compress about 2 inches as well, keeping in mind their smaller, more flexible chest. For infants, press down about 1.5 inches. Pushing too hard can cause injuries, but not pushing hard enough won’t adequately circulate the blood.
Timing and Rhythm for Chest Compressions
The rhythm of the compressions is as important as their depth. You should aim for a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute. An easy way to remember the rhythm is by using the beat of the song "Stayin' Alive" by the Bee Gees. If you’re performing CPR with rescue breaths, give 30 compressions followed by 2 breaths and repeat the cycle.
It's important not to interrupt the compressions for more than a few seconds, even when giving rescue breaths. Continual compressions are key to maintaining circulation until professional help arrives. Ensuring you have the proper technique will give the person a much better chance of recovery.
5. Using CPR in Real-Life Scenarios
Common Situations That May Require CPR
Knowing when to use CPR is as important as knowing how to. Common scenarios include someone collapsing from a heart attack, drowning, or choking. If you find an unconscious person and they aren't breathing, it's time to start CPR. Car accidents and severe allergic reactions can also lead to situations where CPR is necessary.
Being prepared to act in these situations can save lives. Often, the first few minutes are critical, and immediate CPR can double or triple a person's chances of survival. That's why it's vital to recognize when CPR is needed and to act quickly and confidently.
Importance of CPR Training and Certification
While this guide provides a basic understanding of CPR, getting formal training and certification is highly recommended. Certified courses provide hands-on practice and detailed instruction that you can't get from reading alone. They also cover additional important details like using an Automated External Defibrillator (AED).
Certification courses help you feel more confident and ready to help in an emergency. They often include scenarios and practice sessions that mimic real-life situations. By being properly trained, you ensure that you can provide the best care possible in an emergency, giving the person in need the best chance at survival.
Conclusion
CPR is a critical skill that everyone should learn. It empowers you to take action in an emergency and potentially save a life. From understanding the basics, knowing the correct techniques, and practicing real-life application, each step is crucial. The sooner you can start CPR in an emergency, the better the outcome for the person in need.
If you're ready to take comprehensive CPR training in NH, contact us at The First Aid Guy LLC today. Our courses are designed to give you the skills and confidence needed to save lives. Don't wait—equip yourself with these vital skills today.
